Newsroom
News
Contacting the molecular world through graphene nanoribbons
NanoGUNE has its R&D&i management system certified in accordance with the UNE 166002:2014 Standard
Nanoparticles act as enzymes
The result in brief of the EU project ARTEN, lead by Mato Knez (leader of the Nanomaterials group at nanoGUNE) are now available at CORDIS.
The powers of nanoscience in a comic
Los poderes de la nanociencia en cómic
Nanozientziaren botereak komikian
Nanomechanics of pathogenic attachment Uropathogenic Escherichia coli and Human Immunodeciency Virus
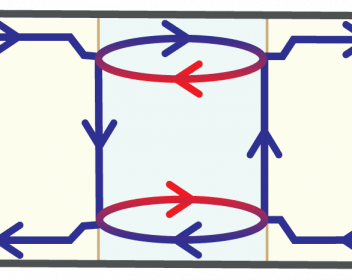
Engineering electron pathways in 2D-topological insulators
In a recent article published in Physical Review Letters researchers from CIC nanoGUNE, the Rudolf Peierls Centre for Theoretical Physics of Oxford, together with colleagues from Wuerzburg and Stanford University reported new insight into the electronic conduction and interference on 2D-topological insulators - an exotic kind of insulators that conduct only at the edge and that could be key for the development of a new generation of electronic devices.
CIC nanoGUNE is participating in two European projects to train young researchers
NanoGUNE is set to participate in two new projects on quantum electronics and hybrid coatings in one of Europe’s most competitive programs, the European Union’s Initial Training Networks (ITN), starting January 2018. Through this participation the center will be receiving nearly half a million euros for each project for the coming four years.
Launch of the “Alliance of Severo Ochoa Centres and Maria de Maeztu Units of Excellence”
The Secretary of State for R&D+i, Carmen Vela, chaired the kickoff meeting of the new Severo Ochoa and Maria Maeztu Alliance of Excellence. The alliance’s target is to internationally promote and strengthen the centres and units accredited with this distinction, to give their research a higher profile.
Agenda
| Mon | Tue | Wed | Thu | Fri | Sat | Sun |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
23
|
24
|
25
|
26
|
27
|
28
|
1
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2
|
3
|
4
|
5
|
6
|
7
|
8
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10
|
11
|
12
|
13
|
14
|
15
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18
|
19
|
20
|
21
|
22
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
23
|
24
|
25
|
26
|
27
|
28
|
29
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
30
|
31
|
1
|
2
|
3
|
4
|
5
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Events
No events
nanoVISUALS
Find events' photos, experimental images, videos, audios, and nanoGUNE's corporate images.